CH592 Setup
Hardware Setup
We'll use the WeActStudio CH592F board. To flash the chip, use WCH-LinkE debugger probe, available on Aliexpress. Note that you need the E variant, for our purpose the old ch549 based one is inadequate. Or you could do away with a probe altogether and use icsp method, as the chip comes with a USB bootloader. See wchisp.
Fix permissions
On Linux, to access the debugger without sudo access you need the following files.
/etc/udev/rules.d/50-wchlink.rules:
# 1a86:8010 WCH Link
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="1a86", ATTR{idProduct}=="8010", OWNER="username"
/etc/udev/rules.d/50-usb-serial.rules:
SUBSYSTEM=="tty", SUBSYSTEMS=="usb", OWNER="username"
Note to replace username. You may have to use relevant idVendor and idProduct if you're using a different hardware version. Run dmesg to find out.
Attach the probe
You need four wires to hook the mcu to the probe.
TCK - PB15
TIO - PB14
And 3V3, GND, power lines.
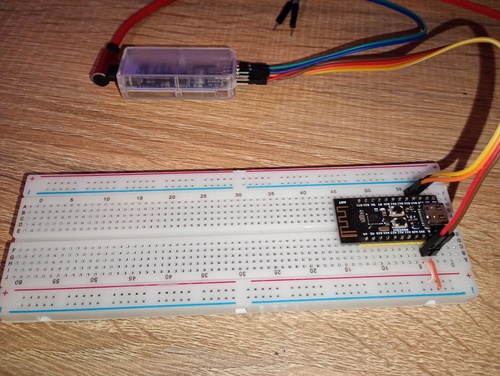
Before using a probe, the icsp must be enabled on the target chip! As the factory setting is to disable by default.
To enable debug use wchisp. Connect the board direct via USB and
wchisp config reset.
Use wlink to program. Run wlink status and it should detect the chip.
Install the toolchain
Download MRS Toolchain. Then extract it. You can do this by (current version V210 as of this writing, otherwise change it):
# cd to downloaded directory
mkdir -p $HOME/.local/opt
tar xvf MRS_Toolchain_Linux_x64_V210.tar.xz -C $HOME/.local/opt
Next, add these programs to your $PATH. For bash users, this can typically be accomplished by:
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.local/opt/RISC-V Embedded GCC12/bin/:$HOME/.local/opt/OpenOCD/OpenOCD/bin/:$PATH"' >> $HOME/.bashrc
The following Makefiles assume you have this installed.
Also make sure you have make and git installed on your system.
Setting up our Makefile SDK
The SDK is provided in Github. The vendor's library is located in EVT/EXAM/SRC/ directory. Create a workspace directory for our projects and put the contents into a dir named vendor. The workspace directory should look like this.
.
├── myapps
│ └── blinky
│ ├── Makefile
│ └── src
│ └── main.c
└── vendor
├── Ld
│ └── Link.ld
├── RVMSIS
│ ├── core_riscv.c
│ └── core_riscv.h
├── Startup
│ └── startup_CH592.S
└── StdPeriphDriver
├── CH59x_adc.c
├── CH59x_clk.c
├── CH59x_flash.c
├── CH59x_gpio.c
├── CH59x_i2c.c
├── CH59x_lcd.c
├── CH59x_pwm.c
├── CH59x_pwr.c
├── CH59x_spi0.c
├── CH59x_sys.c
├── CH59x_timer0.c
├── CH59x_timer1.c
├── CH59x_timer2.c
├── CH59x_timer3.c
├── CH59x_uart0.c
├── CH59x_uart1.c
├── CH59x_uart2.c
├── CH59x_uart3.c
├── CH59x_usbdev.c
├── CH59x_usbhostBase.c
├── CH59x_usbhostClass.c
├── inc
│ ├── CH592SFR.h
│ ├── CH59x_adc.h
│ ├── CH59x_clk.h
│ ├── CH59x_common.h
│ ├── CH59x_flash.h
│ ├── CH59x_gpio.h
│ ├── CH59x_i2c.h
│ ├── CH59x_lcd.h
│ ├── CH59x_pwm.h
│ ├── CH59x_pwr.h
│ ├── CH59x_spi.h
│ ├── CH59x_sys.h
│ ├── CH59x_timer.h
│ ├── CH59x_uart.h
│ ├── CH59x_usbdev.h
│ ├── CH59x_usbhost.h
│ └── ISP592.h
└── libISP592.a
As you may have noticed, most files in the vendor library come with Chinese comments! I generated a python script available here that recursively converts source file comments to English. After copying the script to the workspace directory run it with
python3 ./translate-comments.py ./vendor. Note you would need to install thedeep-translatorpython module via pypi.
The contents of the Makefile and main.c are as follows. (We'll study them in the following article)
main.c:
#include "CH59x_common.h"
void board_led_init(void)
{
GPIOA_SetBits(GPIO_Pin_8);
GPIOA_ModeCfg(GPIO_Pin_8, GPIO_ModeOut_PP_5mA);
}
void board_led_toggle(void)
{
GPIOA_InverseBits(GPIO_Pin_8);
}
void board_led_set(uint8_t set)
{
if (set)
GPIOA_ResetBits(GPIO_Pin_8);
else
GPIOA_SetBits(GPIO_Pin_8);
}
int main()
{
uint8_t s;
SetSysClock(CLK_SOURCE_PLL_60MHz);
board_led_init();
while(1)
{
mDelaymS(100);
board_led_toggle();
mDelaymS(100);
}
}
Makefile:
######################################
# target
######################################
TARGET = ch592_blinky
# ../../
######################################
# building variables
######################################
# debug build?
DEBUG = 1
# optimization for size
OPT = -Os
#######################################
# paths
#######################################
# Build path
BUILD_DIR = build
######################################
# source
######################################
# C sources
C_SOURCES = \
src/main.c \
../../vendor/StdPeriphDriver/CH59x_clk.c \
../../vendor/StdPeriphDriver/CH59x_gpio.c \
../../vendor/StdPeriphDriver/CH59x_pwr.c \
../../vendor/StdPeriphDriver/CH59x_sys.c \
../../vendor/RVMSIS/core_riscv.c \
# ASM sources
ASM_SOURCES = \
../../vendor/Startup/startup_CH592.S
#######################################
# binaries
#######################################
#PREFIX = riscv-none-elf-
#PREFIX = riscv64-elf-
#debian
#PREFIX = riscv64-unknown-elf-
PREFIX = riscv-wch-elf-
CC = $(PREFIX)gcc
AS = $(PREFIX)gcc -x assembler-with-cpp
CP = $(PREFIX)objcopy
SZ = $(PREFIX)size
HEX = $(CP) -O ihex
BIN = $(CP) -O binary -S
#######################################
# CFLAGS
#######################################
# cpu
CPU = -march=rv32imac_zicsr -mabi=ilp32 -msmall-data-limit=8
# For gcc version less than v12
# CPU = -march=rv32imac -mabi=ilp32 -msmall-data-limit=8
# fpu
FPU =
# float-abi
FLOAT-ABI =
# mcu
MCU = $(CPU) $(FPU) $(FLOAT-ABI)
# AS includes
AS_INCLUDES =
# C includes
C_INCLUDES = \
-I../../vendor/StdPeriphDriver/inc \
-I../../vendor/RVMSIS \
-I../../vendor/Core \
-Isrc/include
# compile gcc flags
ASFLAGS = $(MCU) $(AS_INCLUDES) $(OPT) -Wall -fdata-sections -ffunction-sections
CFLAGS = $(MCU) $(C_INCLUDES) $(OPT) -Wall -fdata-sections -ffunction-sections
ifeq ($(DEBUG), 1)
CFLAGS += -g -gdwarf-2
endif
# Generate dependency information
CFLAGS += -MMD -MP -MF"$(@:%.o=%.d)"
#######################################
# LDFLAGS
#######################################
# link script
LDSCRIPT = ../../vendor/Ld/Link.ld
# libraries
LIBS = -lc -lm -lnosys ../../vendor/StdPeriphDriver/libISP592.a
LIBDIR =
LDFLAGS = $(MCU) -mno-save-restore -fmessage-length=0 -fsigned-char -ffunction-sections -fdata-sections -Wunused -Wuninitialized -T $(LDSCRIPT) -nostartfiles -Xlinker --gc-sections -Wl,-Map=$(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).map --specs=nano.specs $(LIBS)
# default action: build all
all: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).elf $(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).hex $(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).bin
#######################################
# build the application
#######################################
# list of objects
OBJECTS = $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/,$(notdir $(C_SOURCES:.c=.o)))
vpath %.c $(sort $(dir $(C_SOURCES)))
# list of ASM program objects
OBJECTS += $(addprefix $(BUILD_DIR)/,$(notdir $(ASM_SOURCES:.S=.o)))
vpath %.S $(sort $(dir $(ASM_SOURCES)))
$(BUILD_DIR)/%.o: %.c Makefile | $(BUILD_DIR)
$(CC) -c $(CFLAGS) -Wa,-a,-ad,-alms=$(BUILD_DIR)/$(notdir $(<:.c=.lst)) $< -o $@
$(BUILD_DIR)/%.o: %.S Makefile | $(BUILD_DIR)
$(AS) -c $(CFLAGS) $< -o $@
#$(LUAOBJECTS) $(OBJECTS)
$(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).elf: $(OBJECTS) Makefile
$(CC) $(OBJECTS) $(LDFLAGS) -o $@
$(SZ) $@
$(BUILD_DIR)/%.hex: $(BUILD_DIR)/%.elf | $(BUILD_DIR)
$(HEX) $< $@
$(BUILD_DIR)/%.bin: $(BUILD_DIR)/%.elf | $(BUILD_DIR)
$(BIN) $< $@
$(BUILD_DIR):
mkdir $@
#######################################
# Program
#######################################
isp: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).bin
wchisp flash $(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).bin
flash: $(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).bin
wlink flash $(BUILD_DIR)/$(TARGET).bin
#######################################
# clean up
#######################################
clean:
-rm -fR $(BUILD_DIR)
#######################################
# dependencies
#######################################
-include $(wildcard $(BUILD_DIR)/*.d)
# *** EOF ***
Building our first example
The example project we created is a blinky example. Run make to build. Assuming you have the toolchain correctly installed it should succeed. Now run
wlink flash build/ch592_blinky.bin